Hackers are using the WordPress mu-plugins (“Should-Use Plugins”) listing to stealthily run malicious code on each web page whereas evading detection.
The approach was first noticed by safety researchers at Sucuri in February 2025, however adoption charges are on the rise, with menace actors now using the folder to run three distinct forms of malicious code.
“The truth that we have seen so many infections inside mu-plugins means that attackers are actively focusing on this listing as a persistent foothold,” explains Sucuri’s safety analyst Puja Srivastava.
“Should-have” malware
Should-Use Plugins (mu-plugins) are a particular sort of WordPress plugin that robotically execute on each web page load while not having to be activated within the admin dashboard.
They’re PHP recordsdata saved within the ‘wp-content/mu-plugins/’ listing that robotically execute when the web page is loaded, and they aren’t listed within the common “Plugins” admin web page except the “Should-Use” filter is checked.
Mu-plugins have authentic use instances comparable to implementing site-wide performance for {custom} safety guidelines, efficiency tweaks, and dynamically modifying variables or different code.
Nonetheless, as a result of MU-plugins run on each web page load and do not seem in the usual plugin record, they can be utilized to stealthily carry out a variety of malicious exercise, comparable to stealing credentials, injecting malicious code, or altering HTML output.
Sucuri has found three payloads that attackers are planting within the mu-plugins listing, which seems to be a part of financially motivated operations.
These are summarized as follows:
redirect.php: Redirects guests (excluding bots and logged-in admins) to a malicious web site (updatesnow(.)internet) that shows a faux browser replace immediate to trick them into downloading malware.
index.php: Webshell that acts as a backdoor, fetching and executing PHP code from a GitHub repository.
custom-js-loader.php: Masses JavaScript that replaces all pictures on the location with express content material and hijacks all outbound hyperlinks, opening shady popups as a substitute.
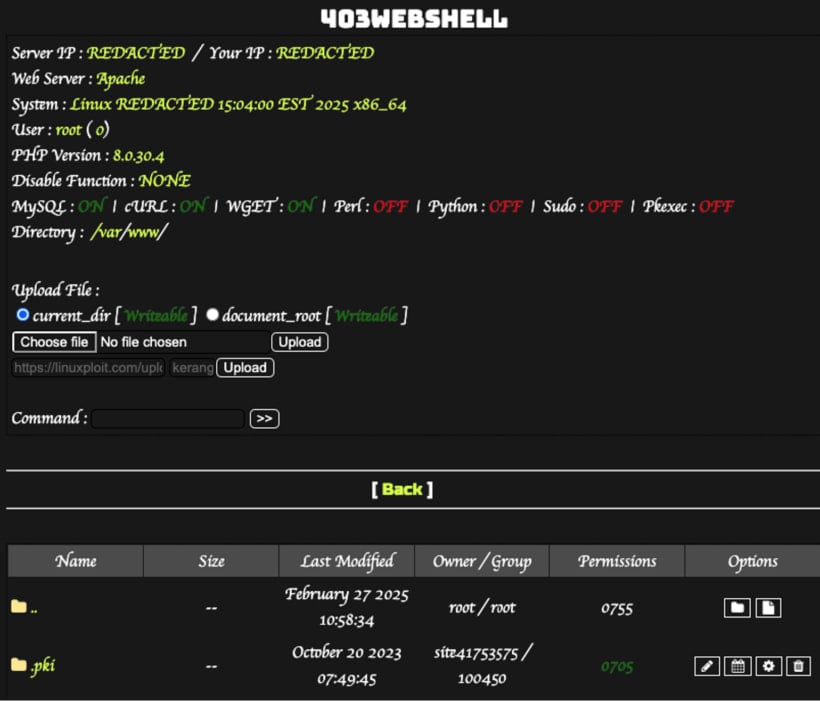 The 403WebShell interface
The 403WebShell interface
Supply: juices
The webshell case is especially harmful because it permits the attackers to remotely execute instructions on the server, steal information, and launch downstream assaults on members/guests.
The opposite two payloads may also be damaging as they harm a web site’s popularity and website positioning scores on account of shady redirections and try to put in malware on customer’s computer systems.
Sucuri has not decided the precise an infection pathway however hypothesizes that attackers exploit recognized vulnerabilities on plugins and themes or weak admin account credentials.
It is suggested that WordPress web site admins apply safety updates on their plugins and themes, disable or uninstall those who aren’t wanted, and shield privileged accounts with robust credentials and multi-factor authentication.
Primarily based on an evaluation of 14M malicious actions, uncover the highest 10 MITRE ATT&CK strategies behind 93% of assaults and learn how to defend in opposition to them.





