CoinMarketCap, the favored cryptocurrency value monitoring website, suffered an internet site provide chain assault that uncovered website guests to a pockets drainer marketing campaign to steal guests’ crypto.
On Friday night, January 20, CoinMarketCap guests started seeing Web3 popups asking them to attach their wallets to the location. Nevertheless, when guests linked their wallets, a malicious script drained cryptocurrency from them.
The corporate later confirmed risk actors utilized a vulnerability within the website’s homepage “doodle” picture to inject malicious JavaScript into the location.
“On June 20, 2025, our safety workforce recognized a vulnerability associated to a doodle picture displayed on our homepage. This doodle picture contained a hyperlink that triggered malicious code by an API name, leading to an sudden popup for some customers when visited our homepage,” reads a press release posted on X.
“Upon discovery, We acted instantly to take away the problematic content material, recognized the basis trigger, and complete measures have been applied to isolate and mitigate the difficulty.”
“We are able to verify all techniques are actually absolutely operational, and CoinMarketCap is secure and safe for all customers.”
Cybersecurity agency c/facet defined that the assault labored by the risk actors someway modifying the API used by the location to retrieve a doodle picture to show on the homepage. This tampered JSON payload now included a malicious script tag that injected a pockets drainer script into CoinMarketCap from an exterior website named “static.cdnkit(.)io”.
When somebody visited the web page, the script would execute and show a pretend pockets join popup exhibiting CoinMarketCap branding and mimicking a respectable Web3 transaction request. Nevertheless, this script was truly a pockets drainer designed to steal linked wallets’ property.
“This was a provide chain assault, which means the breach didn’ goal CMC’s personal servers however a third-party software or useful resource utilized by CMC,” explains c/facet.
“Such assaults are onerous to detect as a result of they exploit trusted parts of a platform.”
Extra particulars concerning the assault got here later from a risk actor generally known as Reywho mentioned that the attackers behind the CoinMarketCap provide chain assault shared a screenshot of the drainer panel on a Telegram channel.
This panel indicated that $43,266 was stolen from 110 victims as a part of this provide chain assault, with the risk actors talking in French on the Telegram channel.
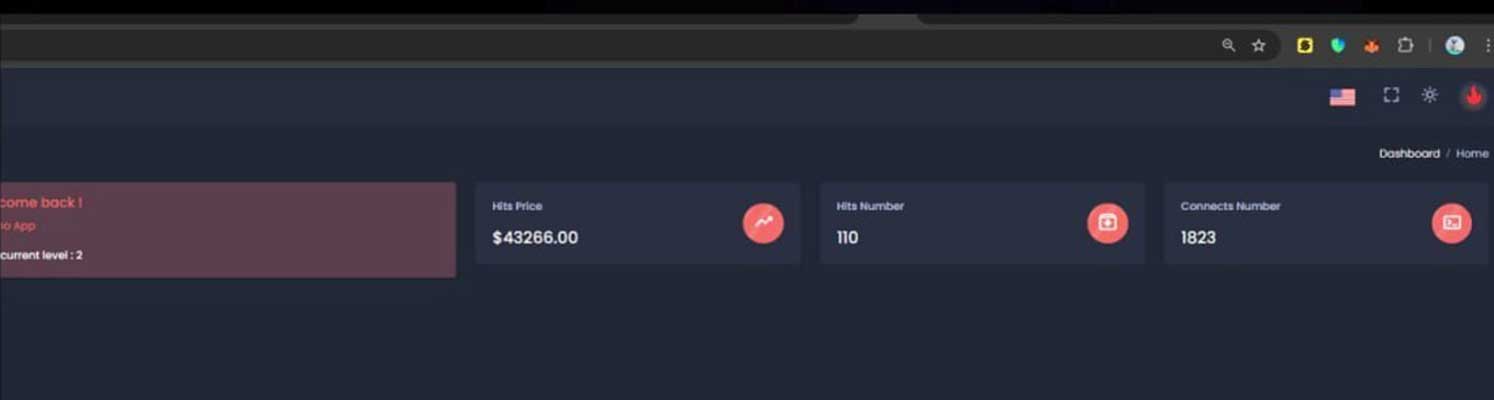 Screenshot of drainer panel shared on Telegram
Screenshot of drainer panel shared on Telegram
Supply: Rey
As the recognition of cryptocurrency has boomed, so has the risk from pockets drainers, that are generally utilized in assaults.
In contrast to conventional phishing, these kinds of assaults are extra typically promoted by social media posts, ads, spoofed websites, and malicious browser extensions that embody malicious wallet-draining scripts.
Experiences point out that pockets drainers stole nearly $500 million in 2024 by assaults concentrating on greater than 300,000 pockets addresses.
The issue has change into so pervasive that Mozilla just lately launched a brand new system to detect pockets drainers in browser add-ons uploaded to the Firefox Add-on repository.
Patching used to imply advanced scripts, lengthy hours, and infinite fireplace drills. Not anymore.
On this new information, Tines breaks down how trendy IT orgs are leveling up with automation. Patch sooner, scale back overhead, and give attention to strategic work — no advanced scripts required.





