Drug mixtures in most cancers remedy and nanomedicine
The multifaceted nature of most cancers necessitates the exploration and use of various remedy modalities. In routine medical apply, sufferers usually bear a mix of interventions, aiming for an optimum therapeutic outcome1. Such situations not solely entail the mixture of two utterly totally different therapeutic modalities (for instance, surgical procedure and chemotherapy), but in addition mix a number of therapeutic sub-options throughout the identical remedy class. For instance, neoadjuvant chemotherapy usually encompasses a cocktail of chemotherapeutic medicine, aiming to realize maximal tumour shrinkage earlier than surgery2. Moreover, drug mixture therapies can complementarily deal with pathways of most cancers development on the degree of most cancers cells, immune cells and/or the tumour microenvironment3,4.
Regardless of the commonly constructive results of mixing totally different chemotherapeutics, mixture remedy is difficult, as variations in physicochemical and pharmacokinetic properties between totally different medicine result in uncoordinated concentrating on, efficacy and toxicity. Therefore, dosing and scheduling an optimum drug mixture routine is troublesome. A number of totally different drug supply programs have been designed and evaluated through the years to assist right this disconnect5. The success of nanomedicines depends on traits that embrace improved drug stability and solubility, focused supply to the pathological website, managed drug launch, and low off-target localization6. The versatile properties of nanocarriers make them appropriate for delivering a plethora of various medicine to diseased tissues. Nanoformulations can moreover be readily engineered to co-encapsulate two or extra medicine to allow co-delivery to the identical goal cell, and/or tissue compartment, on the identical cut-off date—ideally attaining synergistic therapeutic efficacy7. A clinically related instance showcasing the flexibility of nanomedicines to co-encapsulate a number of medicine is Vyxeos. Vyxeos is a liposomal formulation that mixes cytarabine and daunorubicin in a set 5:1 ratio; it’s accepted as a first-line remedy for sufferers affected by acute myeloid leukaemia (AML) with myelodysplasia-related modifications, in addition to for therapy-related AML. The co-encapsulation of the 2 medicine at this mounted synergistic ratio produces clinically substantial enhancements in general survival in sufferers with a really poor prognosis and really excessive medical need8.
Mixture methods haven’t solely been profitable for the co-delivery of chemotherapy brokers, but in addition for the mixture of different drug lessons. For instance, immunomodulatory drug mixtures have been utilized in relapsing-remitting a number of sclerosis. On this context, Copaxone is a heterogenous combination of hundreds of thousands of various polypeptides, with every polypeptide consisting of 4 amino acids co-synthesized in mounted molar ratios however at random sequences. The immunomodulatory impact of Copaxone is attributed to the similarities of its chemical composition to the myelin primary protein—one of many autoantigens implicated in a number of sclerosis. Copaxone acts as an immunosuppressor and helps to attenuate pathological inflammatory processes in a number of sclerosis lesions, thereby decreasing the frequency of relapses in sufferers with relapsing-remitting a number of sclerosis9,10.
The constructive impact of co-encapsulating two compounds in a single (nano)formulation has additionally been explored in mRNA supply. Particularly, two mRNAs encoding for various fluorescent proteins have been encapsulated in lipid nanoparticles both collectively or individually, in mounted ratios. Co-encapsulation enabled the supply of each mRNAs into the identical cells on the desired ratio, whereas separate encapsulation led to dissimilar mobile uptake and variable protein expression11. Equally, a bottlebrush polymer prodrug was not too long ago reported during which the three a number of myeloma medicine bortezomib, pomalidomide and dexamethasone are co-formulated. The therapeutic efficacy of administering a statistical combination of three-drug polymer nanotherapy with synergistic drug ratios was in contrast with that of co-administering three single-drug polymer prodrugs at an identical quantities. The three-drug co-formulation potently outperformed single-drug co-administration, even when decrease complete doses of the previous have been applied12,13.
Regardless of the broadly anticipated benefits of nanomedicine-based mixture remedy, its advantages haven’t but been analysed in a complete and quantifyable method. Right here we subsequently got down to systematically research the worth of multi-drug most cancers nanomedicine mixture remedy in contrast with free medicine, free drug mixtures and single nanodrug remedy in pre-clinical mouse fashions. To this finish, we screened the pre-clinical literature and recognized 742 distinctive manuscripts, of which 273 research enabled us to comprehensively evaluate therapeutic efficacy outcomes (tumour progress inhibition and survival) of multi-drug nanotherapy to a few related management teams: single free drug remedy, free drug mixture remedy and single-drug nanotherapy. We additionally in contrast the efficacy of dual-drug nanomedicine co-formulation versus two single-drug nanomedicines. For complete understanding, we lastly additionally analysed the affect of remedy schedule, tumour kind, drug resistance, immunological standing and concentrating on technique on the added worth of multi-drug most cancers nanomedicine mixture remedy.
Systematic evaluation of ‘mixture most cancers nanotherapy’ in literature
All out there analysis papers on mixture nanotherapy have been collected by way of an intensive literature search within the scopus.com database. This search, primarily based on three teams of related key phrases (Fig. 1a and Supplementary Fig. 1), yielded 882 outcomes addressing multi-drug most cancers nanomedicine mixture remedy. After making use of the related exclusion standards, a complete of 273 appropriate manuscripts (see Supplementary Desk 1) have been chosen for in-depth evaluation (Fig. 1b).
Fig. 1: Meta-analysis methodology.
a, Search phrases used on scopus.com to establish analysis articles specializing in multi-drug nanomedicine mixture remedy. b, Inclusion versus exclusion of research specializing in most cancers nanomedicine mixture remedy. ‘Different’ exclusion standards embrace causes similar to use of non-murine animal fashions, and investigation of ailments apart from most cancers. c, Pie charts primarily based on knowledge collected from the 273 included analysis articles illustrate particulars relating to the kind of drug used, route of administration, nanocarrier formulation, injection protocol, most cancers mannequin and most cancers kind. The allotted teams (listed beneath the charts) are represented within the clockwise path, ranging from the highest. Admin., administration; AB, antibody.
By digging into experimental particulars, we recognized a number of attention-grabbing research traits (Fig. 1c). Doxorubicin was by far most used drug, usually serving as a prototype drug to validate the impact of the mixture remedy upon combining it with a second and/or third drug. This discovering is in keeping with present medical apply, as doxorubicin could be very broadly used and was traditionally the primary chemotherapy drug that was accepted in liposomal formulations (that’s, Doxil/Myocet)14,15. Different medicine which were very extensively used are paclitaxel and platinum-based medicine, in keeping with their widespread use as first- or second-line chemotherapy for numerous cancers within the clinic16. Concerning route of administration, the evaluated nanochemotherapeutics are largely injected intravenously, which is certainly the most typical administration route in medical practice17. Contemplating the composition materials of nanocarriers, lipids and polymers have been probably the most abundantly used. Considerably surprisingly, there have been barely extra papers on polymeric mixture nanotherapy than on liposomal multi-drug remedy, despite the truth that most medical merchandise are primarily based on liposomes (for instance, Doxil, DaunoXome, DepoCyt and Onivyde)5. With respect to drug loading and injection routine, formulations that concurrently contained two medicine have been extra frequent compared to a mixture of single-loaded nanomedicines.
By way of the most cancers fashions employed to guage mixture nanotherapy, most pre-clinical fashions have been xenografts, during which human most cancers cell traces and patient-derived most cancers cells are inoculated in immunodeficient mice (Fig. 1c). These fashions have the limitation that they don’t permit for full consideration immunological (nano/chemo)remedy effects18. Syngeneic allograft tumour fashions will be grown in immunocompetent mice, however don’t permit to be used of human most cancers cells19. With regard to intrinsic drug sensitivity, nearly all of research have been performed in chemotherapy-sensitive fashions, and solely 14% of experiments targeted on mixture nanotherapy as a method to counteract multi-drug drug resistance.
Lastly, in keeping with the lengthy custom in nanomedicine to focus on breast most cancers (in all probability because of ease of mannequin growth, in addition to vast prevalence within the world inhabitants)20, the 4T1 triple-negative breast most cancers mannequin was discovered to be the by far most incessantly used tumour mannequin (Fig. 1c). Its prevalence was greater than twice as excessive as that of the second-highest-used mannequin. The 4T1 mannequin has a number of traits that make it a pretty experimental mouse mannequin: it’s a sturdy, quickly rising, syngeneic and orthotopic mannequin that may metastasize spontaneously, and carefully resembles human triple-negative breast cancer21.
Multi-drug most cancers nanotherapy boosts remedy end result
To guage the efficacy of multi-drug mixture nanotherapy, we quantified the therapeutic efficacies of: (1) single free medicine, (2) free drug mixtures, (3) single nanodrugs and (4) mixture nanodrugs, and in contrast them in opposition to tumour progress noticed within the PBS/automobile management group (Fig. 2a,b). From this evaluation, it may be robustly concluded that: (i) drug mixtures are virtually at all times higher than single therapies—each without spending a dime drug and for nanomedicine-based therapies. Totally different medicine can goal totally different pathways, leading to improved remedy outcomes22; (ii) the mixture of two free medicine is extra environment friendly than single free medicine, decreasing tumour progress to 53.4% versus 66.9% of controls, respectively; (iii) the mixture of medication delivered by nanomedicines very effectively suppresses tumour progress, to solely 24.3% on management tumours progress. For single-drug nanotherapy, tumour progress is decreased to 54.3% of controls.
Fig. 2: Efficacy evaluation of multi-drug most cancers nanotherapy.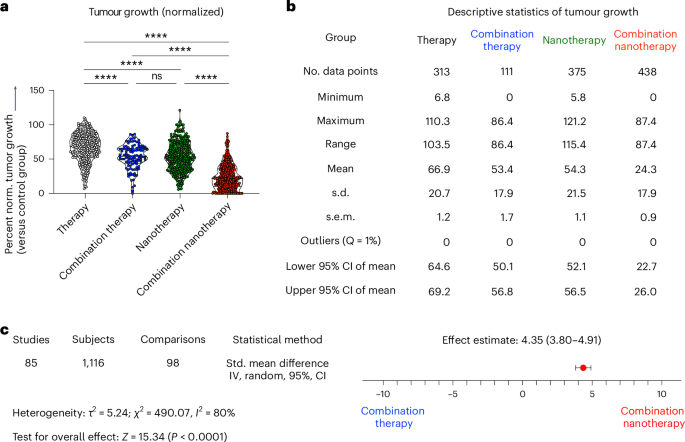
a, Direct comparability of the antitumor efficacy of (1) free medicine alone, (2) free drug mixture remedy, (3) nanodrugs alone, and (4) nanodrug mixture remedy. Our evaluation demonstrates that multi-drug nanomedicines outperform the opposite remedy teams. Statistical significance was assessed by way of a two-sided Kruskal–Wallis check with Dunn’s correction for a number of comparisons (****P < 0.0001, ***P < 0.001, **P < 0.01, *P < 0.05, ns, not important). b, Overview of descriptive statistics among the many 4 teams demonstrated a 42.6%, 29.1% and 30.0% further tumour inhibition enhancement for mixture nanotherapy versus single free-drug, free drug mixture remedy, and single-drug nanotherapy, respectively. c, Meta-analysis evaluating mixture remedy to mixture nanotherapy. Pooled outcomes from 98 comparisons with 1,116 mice, indicated an impact in favour of mixture nanotherapy. Heterogeneity exams confirmed excessive heterogeneity, with l2 = 80%. This in all probability outcomes from the intrinsic selection between the included research relating to tumour fashions, therapies, remedy schedules and nanoparticle designs. Meta-analysis was carried out by measuring the standardized (Std.) imply distinction, utilizing an inverse variance (IV) and random results mannequin. Heterogeneity between the teams was investigated utilizing τ2 and χ2 exams and the I2 index.
Upon learning the ends in Fig. 2a,b extra comprehensively, we discover that: (iv) in contrast with free drug remedy, single-drug formulation in nanomedicines enhances the remedy end result by 12.6%. Carriers can be utilized to ship a plethora of therapeutics, similar to hydrophilic or hydrophobic medicine, small drug molecules, peptides and proteins. Nanomedicine encapsulation is understood to boost drug circulation half-life and goal website accumulation, thereby selling therapeutic outcomes in mouse models23. (v) Combining two medicine in free kind is as efficient as single-drug nanotherapy. The expansion inhibition induced by each regimens was discovered to be virtually comparable, that’s, 53.4% and 54.3% of controls. Lastly, and most significantly, (vi) mixture nanotherapy outperformed all different regimens, with an extra 42.6%, 30% and 29.1% stronger inhibition of tumour progress in contrast with single free-drug remedy, single-drug nanotherapy and free drug mixture remedy, respectively. This in all probability comes from nanocarriers’ means to include medicine in outlined ratios and permit for managed and sustained drug release24. One of many main causes behind mixture nanotherapy’s success lies in its improved circulation half-life and biodistribution profile. Particularly, nanomedicines have been proven to lengthen the circulation half-life of drug molecules by ninefold, they usually allow fivefold-higher drug accumulation in tumours in contrast with their free drug counterparts (Supplementary Fig. 2). Moreover, nanomedicine co-encapsulation aligns temporal and spatial concentrating on to the identical cell and/or identical tumour compartment, thereby selling synergy7. Additional evaluation was carried out to guage whether or not there are variations in outcomes between research that investigated potential synergy between the used medicine and those who didn’t. Out of the 273 research, 86 actively investigated synergistic interactions of drug mixtures. Nevertheless, no discernible distinction might be noticed between the 2 teams (Supplementary Fig. 3a,b). However, it ought to be famous that in all research besides one, the overall drug dose was the identical for monotherapy and mixture remedy, which implies that a better general drug dose was used within the mixture remedy group. Potential synergies in drug mixtures may ultimately be exploited to assist cut back general drug doses, they usually may help in bettering drug compliance and tolerability, making mixture remedy a simpler and safer possibility general.
With respect to the mixture set-up, most research chosen a mix of two medicine, whereas a few of them even tried to mix three medicine. It was discovered that the added worth of combinatorial nanotherapy was transferable to each two- and three-drug mixture set-ups. As in contrast with two-drug mixture nanotherapy, three-drug mixture nanotherapy was discovered to supply a further 6.5% discount of tumour progress (Supplementary Fig. 4a,b).
The remedy research analysed on this work displayed a excessive diploma of heterogeneity with regard to planning and executing of the animal experiments. To handle this, the research have been additional divided in keeping with (1) general remedy length, (2) the variety of complete remedy administrations, (3) the variety of days between the ultimate remedy administration and the evaluation of the tumour’s progress, and (4) time elapsed from the inoculation of the most cancers cells till demise of the management group (Supplementary Fig. 5). In all of those subgroup analyses, mixture nanotherapy clearly prevailed, displaying superior efficiency by way of tumour progress inhibition than all different remedy teams (Supplementary Figs. 6–9).
Mixture nanotherapy additionally resulted in one of the best general survival of particular person mice (Supplementary Fig. 10a). Following the identical traits as for tumour progress inhibition, single free drug remedy ends in the shortest median general survival, adopted by single-drug nanotherapy and free drug mixture remedy. Mixture nanotherapy clearly offered with probably the most beneficial survival outcomes. To specify, in 87 circumstances of utilizing mixture nanotherapy, 16% achieved full survival of the entire cohort by the top of the experiment, in contrast with solely 2% of research for the single-drug nanotherapy group. For single free drug remedy and free drug mixture remedy, long-term survival was 0% within the research included on this evaluation (Supplementary Fig. 10b).
Based mostly on these outcomes, it may be concluded that nanomedicines potentiate the efficacy of drug mixtures. To substantiate this conclusion, we performed an precise meta-analysis evaluating the remedy efficacy of mixture nanotherapy versus the mixture remedy. To this finish, tumour sizes, commonplace deviations and animal group sizes from mice handled with free drug cocktails (group 2) versus mixture nanotherapy (group 4) have been extracted from the tumour progress curves and inserted into the meta-analysis software program RevMan25. This meta-analysis end result gives the standardized imply distinction, which is a statistical parameter to measure impact sizes, evaluating free drug mixture remedy and mixture nanotherapy; it’s expressed as each numbers and a forest plot (Fig. 2c). Every comparability presents an impartial strictly standardized imply distinction, which leads to an general common of 4.35 in favour of mixture nanotherapy—clearly demonstrating advantages over non-nanomedicine-based mixture remedy. By exploring this evaluation in additional element, 22 comparisons gave no estimable impact dimension because of tumour volumes or commonplace deviations being zero, and so have been subsequently excluded. Out of the 98 comparisons included, eleven comparisons confirmed no impact in both path, whereas one comparability confirmed an impact dimension in favour of free drug mixture remedy. The remaining 86 comparisons confirmed a transparent and extremely important good thing about mixture nanotherapy versus free drug mixture remedy (Fig. 2c, Supplementary Desk 2 and Supplementary Fig. 11).
To this point the idea of mixture nanotherapy has led to the medical approval of Vyxeos. Initially, the usual remedy routine for sufferers with AML concerned every day infusion of daunorubicin mixed with a steady infusion of cytarabine (3 + 7). This commonplace remedy led to as much as 80% remission in youthful sufferers, and to 60% in adults; nonetheless, solely 30% of all sufferers achieved long-term disease-free survival. A number of methods have been explored to boost remedy outcomes, together with dose and administration schedule modifications, or including a 3rd drug, each of which didn’t end in elevated general survival. Pharmacokinetic and dynamic investigations of cytarabine and daunorubicin confirmed that synergistic ratios couldn’t be maintained as a result of these medicine have very totally different physicochemical properties, leading to very totally different biodistributions, goal website accumulations and goal cell uptakes26. A liposomal formulation co-encapsulating each medicine at synergistic ratios was ultimately developed, guaranteeing environment friendly cytarabine and daunorubicin co-delivery to the identical physique compartments and goal cells. In a vital part medical III research, a set 5:1 mixture of the 2 medicine—in contrast with the usual 3 + 7 remedy in sufferers with AML—led to a rise in remission fee, in addition to to a substantial prolongation of each event-free and general survival8,27. Importantly, this trial additionally illustrated that mixture nanotherapy supplied improved efficacy at a decrease cumulative drug dose in contrast with free drug mixture therapy5.
The above medical observations are in keeping with our outcomes of pre-clinical knowledge evaluation, compellingly indicating that future most cancers remedy methods ought to embrace multi-drug mixture nanotherapy. To corroborate this notion, we expanded our evaluation in particular subgroups of the initially analysed cohort, aiming to reply the next questions: is co-encapsulation of two medicine in a single nanomedicine formulation extra useful than two medicine administered in two separate nanocarriers? Which drug kind mixture works greatest for multi-drug nanomedicine software? Is there a superior nanocarrier materials? Is lively nanomedicine tumour concentrating on higher than passive tumour concentrating on? Does PEGylation improve mixture nanotherapy outcomes? Do all tumour varieties profit equally from mixture nanotherapy?
Nanomedicine co-delivery improves mixture remedy end result
Mixture remedy will be utilized in two other ways: co-delivery (that’s, simultaneous administration of two medicine which can be co-encapsulated in the identical formulation) and separate supply (that’s, two medicine are individually encapsulated, and two formulations are co-injected or sequentially administrated). After subdividing research on the idea of the mixture remedy technique used, we discovered that the majority research used co-delivery relatively than separate supply, and—importantly—that co-delivery outperformed separate supply (**P = 0.0016) (Fig. 3a). A direct comparability of research that carried out each co-delivery and separate supply in the identical experiment revealed that in all circumstances besides one, co-encapsulation considerably outperformed separate encapsulation by way of tumour progress inhibition (***P = 0.0002) (Fig. 3b).
Fig. 3: Multifactorial evaluation of multi-drug most cancers nanomedicine.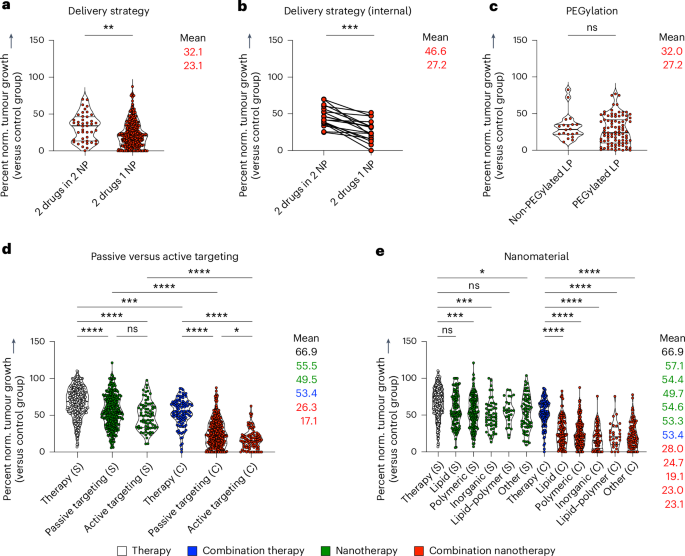
a, Comparability of two frequent administration regimens together nanotherapy, displaying that co-delivery (that’s, two medicine in the identical nanoformulation) outperforms separate supply (that’s, two medicine in two separate nanoformulations). b, Direct comparability of research investigating co-encapsulation versus separate encapsulation in the identical set-up, displaying that in all circumstances besides one, co-encapsulation achieves considerably higher tumour progress inhibition. c, PEGylation didn’t have an effect on the result of multi-drug most cancers nanomedicine. d, Passive versus lively concentrating on of single-drug and multi-drug nanotherapy signifies a development in direction of improved tumour progress discount for lively concentrating on. e, Comparability of generally used drug supply formulations revealed that just about all nanomaterial platforms can enhance single- and multi-drug antitumor therapies. All imply values, from high to backside, correspond with the violin plots from left to proper. Statistical significance was assessed by two-tailed Mann–Whitney check (a–c), and a two-sided Kruskal–Wallis check with Dunn’s correction for a number of comparisons (d,e) (****P < 0.0001, ***P < 0.001, **P < 0.01, *P < 0.05). NP, nanoparticle; LP, lipid-based nanoparticle.
Co-encapsulation will increase the potential for two medicine coming into the identical cell on the identical time in an optimized drug-to-drug ratio12. It thus creates an excellent framework for attaining synergistic anti-tumour results, thereby boosting antitumor exercise and explaining the outcomes of the analysis24. Though two single-loaded nanoparticles can attain tumour compartments concurrently, it’s fairly unlikely that they’re able to obtain ratiometric dosing on the single-cell degree, as already confirmed for small molecules and nucleic acids11,13. Except for most cancers cells, different kinds of cells additionally have to be focused concurrently to advertise synergistically improved anti-tumour efficacy. A number of research have already proven that antigens and immunostimulatory adjuvants, similar to oligodeoxynucleotides, should be delivered in the identical automobile to make sure co-localization in antigen-presenting cells to induce sturdy antigen-specific immune responses28. When the intention is to prime the tumour microenvironment in addition to ship cytotoxic medicine, co-encapsulation is probably not important for improved outcomes29,30,31. It’s because decreasing bodily boundaries, such because the dense extracellular matrix, might require totally different timing and a number of remedy cycles for optimum efficacy32,33. Nonetheless, from the views of mental property, pharmaceutical manufacturing and simple medical translation, one may argue that dual-drug co-encapsulation stays preferable even in such circumstances.
We subsequent in contrast lipid-based nanomedicines with and with out PEG to look at whether or not stealth coatings have a constructive affect on mixture nanotherapy end result. PEGylated formulations confirmed a slight however insignificant enhance in tumour progress suppression (nsP = 0.2808) (Fig. 3c). PEGylation is extensively carried out preclinically and clinically to defend nanoparticles in opposition to aggregation, opsonization and phagocytosis34. PEGylation, nonetheless, additionally has downsides, together with induction of anti-PEG antibodies, non-biodegradability, a chronic whole-body clearance time of the polymer, undesired side-product formation, and discount of drug uptake by goal cells35,36. Furthermore, for sure most cancers varieties—and significantly for non-solid tumours—PEGylation might not essentially add a lot worth, as exemplified by the truth that the dual-drug anti-leukaemia nanomedicine Vyxeos will not be PEGylated. The professionals and cons of nanoparticle PEG coating are typically known as PEG dilemmas, and numerous methods have been carried out to beat them37,38.
One other classical nanomedicine dilemma pertains to using lively concentrating on ligands. To handle this, we immediately in contrast the therapeutic efficacy of free drug single and mixture remedy with that of nanotherapies using both passive or lively concentrating on, together with each single-drug and nanomedicine mixture therapies (Fig. 3d). Passive concentrating on of single nanodrugs resulted in statistically important enhancement of tumour progress inhibition in contrast with single free drug remedy (P < 0.0001) (Fig. 3d). Actively focused single-drug nanotherapy additionally outperformed single free drug remedy, but it surely was not statistically superior to passive concentrating on. With respect to mixture remedy, passively focused dual-drug nanomedicines produced a extremely important enchancment in tumour progress inhibition in contrast with each free drug mixture remedy and single-drug passive nanotherapy (P < 0.0001) (Fig. 3d). Actively focused dual-drug nanomedicine remedy was discovered to be much more environment friendly, outperforming the entire different teams, together with passively focused multi-drug nanotherapy (*P = 0.0401) (Fig. 3d). In precept, lively concentrating on is a really interesting idea; nonetheless, because of ligand ornament procedures, nanoparticles might lose a few of their stealthy character. This will cut back plasma circulation instances, because the modified nanoparticles usually tend to be acknowledged by phagocytes earlier than reaching the goal website and cell39. If ligand-modified nanomedicines do handle to effectively attain tumour compartments, lively concentrating on is anticipated to be beneficial for dual-drug remedy, as the 2 medicine can then certainly be delivered into most cancers cells on the meant synergistic ratio.
We subsequent in contrast totally different nanocarrier supplies as platforms for tumour-targeted drug supply. Drug encapsulation in lipidic, polymeric, inorganic and lipid–polymer-hybrid supplies in all circumstances resulted in improved therapeutic outcomes in contrast with free drug administration; nonetheless statistically important variations have been solely noticed for polymeric (***P = 0.0003), inorganic (***P = 0.0006) and ‘different’ supplies (*P = 0.0124) (Fig. 3e). In dual-drug mixture set-ups, all nanomaterial platforms decreased tumour progress considerably in contrast with free drug mixtures (Fig. 3e). No important variations have been noticed among the many totally different service supplies evaluated. We additionally explored the affect of the drug lessons (co-)administrated in nanocarriers. For that function, we fractionated the research in our evaluation primarily based on all frequent main drug used, that’s, anthracyclines, taxanes, platinum-based medicine, camptothecin (and derivatives), antimetabolites and tyrosine kinase inhibitors. We discovered that in all of those circumstances, mixture nanotherapy considerably elevated the efficacy of tumour progress inhibition by an extra 41.6% in contrast with set-ups during which these main medicine have been administered alone (Supplementary Fig. 12). Altogether, these detailed sub-analyses clearly present that multi-drug nanomedicine is beneficial over all different regimens, together with individually administered nanotherapy mixtures, and that these useful results are corroborated in research taking a look at passive versus lively concentrating on, at supply by way of totally different nanocarrier materials, and encapsulation of various therapeutic cargos.
Multi-drug most cancers nanomedicine efficacy in numerous tumour fashions
To guage whether or not the advantage of nanomedicine mixture remedy is preserved amongst totally different tumour fashions, research have been systematically sorted in keeping with the tumour mannequin used. The remedy cohorts have been once more subdivided in single free drug remedy, single-drug nanotherapy, free drug mixture remedy, and mixture nanotherapy (Fig. 4). Compared to untreated management, single-drug remedy confirmed the bottom tumour progress discount efficacy all through all tumour fashions (58.9–81.2%; Fig. 4a), with pores and skin, cervix, mind and liver most cancers exhibiting the very best (albeit statistically insignificant) response charges, adopted by free drug mixture remedy (48.7–59.8%; Fig. 4b) and single-drug nanotherapy (48.1–64.5%; Fig. 4c). Of observe, single-drug nanotherapy was discovered to be superior to mixture remedy in 5 out of the ten most cancers fashions (Fig. 4b,c). Most significantly, mixture nanotherapy confirmed the by far largest discount in tumour progress for all tumour varieties included, with a big proportion of circumstances even attaining full remission by the top of the experiment (17.3–29.4%; Fig. 4d).
Fig. 4: Evaluation of multi-drug nanomedicine remedy efficacy in numerous most cancers varieties.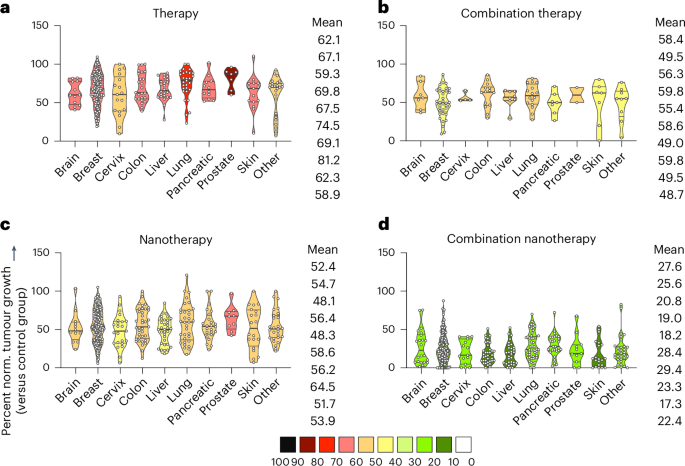
Totally different tumour fashions have been in contrast for every group. Remedies have been divided into single free drug remedy, free drug mixture remedy, single-drug nanotherapy and mixture nanotherapy. In every panel, imply normalized tumour progress discount values are colour-coded. From high to backside, the imply values for the totally different teams correspond to the violin plots from left to proper. a, Single free drug remedy confirmed the bottom tumour discount efficacy all through all fashions. b, Free drug mixture remedy improved the therapeutic response in contrast with single free drug remedy in all most cancers varieties. c, Single-drug nanotherapy enhanced single free drug remedy to an identical extent as free drug mixture remedy. d, Mixture nanotherapy achieves maximal tumour discount throughout all tumour varieties, clearly outperforming the opposite three regimens. Information are offered as violin plots depicting the imply, vary, and 25%, 50% and 75% percentiles.
As drug resistance is a serious reason behind remedy failure in case of chemotherapy in medical apply, we subsequent assessed whether or not the advantage of multi-drug nanotherapy is noticed in each delicate and resistant tumour fashions. Though delicate tumours have been aware of all remedies by comparability with single free drug remedy, resistant tumours solely confirmed a statistically important response to mixture nanotherapy, decreasing tumour progress by 43.9% in contrast with single free drug remedy (Fig. 5a). But, it must be acknowledged that the dearth of statistical significance between the free drug remedy and free drug mixture remedy teams could be a matter of smaller pattern dimension. Both method, in each delicate and resistant tumour fashions, mixture nanotherapy outperformed free drug mixture remedy (Fig. 5a). Lastly, we evaluated whether or not remedy outcomes differ between xenograft fashions (that’s, human tumours grown in immunodeficient mice) and allograft fashions (that’s, mouse tumours grown in immunocompetent mice). Meta-analysis of printed datasets clearly exhibits that multi-drug nanotherapy is best in each mannequin system set-ups, statistically outperforming all different remedy teams (Fig. 5b).
Fig. 5: Evaluation of (nano)drug mixture remedy in delicate versus resistant and xenograft versus allograft tumours.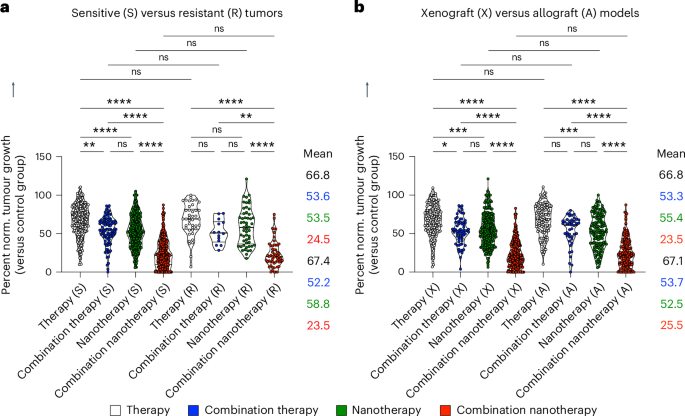
a, Delicate and resistant tumours are each handled most effectively by mixture nanotherapy. For resistant tumours, free drug mixture remedy and single-drug nanotherapy confirmed no profit over single free-drug remedy. Multi-drug mixture nanotherapy was the one remedy that considerably decreased tumour progress in resistant fashions. b, In xenograft versus allograft fashions, remedy regimens produced very comparable efficiency. In each circumstances, mixture nanotherapy was discovered to be the by far the simplest remedy. Information are offered as violin plots depicting the imply, vary, and 25%, 50% and 75% percentiles. Imply values, from high to backside, correspond with the violin plots from left to proper. Statistical significance was decided by a two-sided Kruskal–Wallis check with Dunn’s correction for a number of comparisons (****P < 0.0001, ***P < 0.001, **P < 0.01, *P < 0.05).
Future instructions of multi-drug most cancers nanomedicine
This meta-analysis demonstrates a statistically important good thing about mixture anti-cancer nanotherapy over free drug mixture remedy in pre-clinical mouse fashions (Fig. 2). One clear cause for this useful end result is undoubtfully the flexibility of nanocarriers to enhance the circulation time and goal website accumulation of drug molecules (Supplementary Fig. 2). This profit was constantly noticed throughout totally different tumour varieties and experimental settings (Figs. 3–5 and Supplementary Figs. 3–9). Furthermore, and arguably most significantly, our meta-analysis showcases that co-loading two totally different medicine throughout the identical nanomedicine formulation is statistically superior to the co-administration of two single-drug-loaded nanomedicines (Fig. 3a,b). These findings corroborate ongoing translational efforts in direction of increasing using combinatorial nanomedicines for multi-drug supply.
The result of our meta-analysis ought to be interpreted with care. Publication bias is an element that shouldn’t be neglected, as many researchers decide out from publishing unfavorable outcomes. Normally, we discovered that mixture remedy is best than monotherapy, for each free drug and for nanodrug remedies; nonetheless, we additionally recognized 4 circumstances during which monotherapy carried out higher than mixture remedy, and 17 circumstances during which mixture nanotherapy was much less efficient than single-drug nanotherapy. Nonetheless, this concern is obvious even in research specializing in single-drug nanotherapies, the place researchers might solely publish constructive outcomes relating to the anti-cancer efficacy of a single-drug nanomedicine intervention. Consequently, publication bias appears to have an effect on each the single-drug and the multi-drug nanotherapy teams equally in our comparative evaluation.
When translating outcomes from mice to people, you will need to recognize the appreciable interspecies variations, particularly by way of nanoparticle circulation half-life in blood. Mice usually have sooner metabolism charges and shorter circulation instances than people. Thus, nanoparticles could also be cleared sooner from the blood in mice, probably resulting in discrepancies of their efficacy advantages when translating findings to human purposes. Superior research involving non-human primates might higher inform pharmacokinetic assumptions about human responses.
To maneuver the sector ahead and guarantee translational affect, you will need to rigorously think about the circumstances during which multi-drug supply is useful and wanted, versus these during which it’s conceptually inappropriate. For most cancers chemotherapy, a number of situations will be envisaged during which multi-drug supply provides worth. Co-delivering two totally different cytotoxic medicine to and into the identical goal cell at a synergistic ratio is viable and helpful, as evidenced by the profitable product growth and medical approval of the frontrunner double-drug nanoformulation Vyxeos. This non-PEGylated liposome, which comprises daunorubicin and cytarabine in a 5:1 ratio, effectively targets and kills leukaemia cells upon intravenous administration, and it creates important added worth for sufferers, with an enchancment in median general survival from six months for daunorubicin and cytarabine in free kind to 10 months for Vyxeos (HR = 0.69; P = 0.003)8. When co-administered in free kind, due to the totally different physicochemical and pharmacokinetic parameters of daunorubicin and cytarabine, it appears chanceless to realize synergistic ratios in goal cells, even when intravenously administered at a 5:1 dose. If two single-drug-loaded liposomes could be administered at a 5:1 dose, the query is what number of of these would ultimately find yourself in that ultimate ratio in the identical leukaemia goal cell within the blood stream or within the bone marrow. For 3-drug chemotherapy mixtures, mathematical modelling has proven that chances are high >10 increased to realize synergistic drug ratios in goal cells when co-formulating medicine in nanomedicines versus co-administering single-drug nanomedicines13. For double-drug formulations, the mathematical probabilities might be considerably decrease, however actually nonetheless excessive sufficient to supply a major and clinically significant enhance in therapeutic end result.
When transiting from haematological to strong cancers, the multi-drug supply scenario turns into very totally different. Within the case of haematological malignancies, like leukaemia, liposomes have fairly good entry to leukaemia cells within the blood stream and bone marrow, significantly if they don’t seem to be PEGylated (as within the case of Vyxeos). To optimally attain non-haematological strong tumours and metastases, nanomedicines are usually PEGylated, as this will increase circulation instances and tumour concentrations. Nevertheless, PEGylation can even skew the uptake of nanoparticles away from most cancers cells, in direction of tumour-associated macrophages. For multi-drug supply, which means synergistic ratios are probably delivered to the tumour compartment as an entire, however to not particular person tumour cells, the place pharmacological synergy is required probably the most. Nonetheless, the outcomes of our meta-analysis present that even within the case of strong tumour concentrating on, nanomedicine co-delivery is superior over co-administration of two single-drug-loaded nanomedicines (Fig. 3a,b). In keeping with the above reasoning on the significance of most cancers cell uptake versus tumour-associated macrophage uptake of multi-drug-loaded nanomedicines, we discovered no statistically important added worth of PEGylation on therapeutic efficiency (Fig. 3c). Additionally, in settlement with this, we did discover a statistically important added worth of lively over passive concentrating on in case of nanomedicine mixture remedy, which was not noticed in case of lively versus passive concentrating on with single-drug-loaded nanomedicines (Fig. 3d). You will need to consider on this regard that lively concentrating on usually solely improves the stability between most cancers cell versus macrophage uptake, and never the general ranges of nanomedicine tumour accumulation40,41,42. Accordingly, within the case of multi-drug nanomedicine, the place transportation of synergistic quantities of chemotherapeutic medicine to and into most cancers cells is essential, lively concentrating on is recognized right here as an necessary enabler.
The added worth of multi-drug most cancers nanomedicine crucially depends upon the mechanism of motion of the brokers which can be being co-delivered. When combining a classical chemotherapy drug with a tumour microenvironment-modulating or immune-activating agent, it appears pointless to co-formulate each brokers in the identical nanoparticle. There could also be mental property-related causes or different translationally related arguments for doing so (for instance, having to carry out toxicology research and part I trials for only one double-drug nanoformulation versus for 2 single-drug nanomedicines), however from a pure pharmacological standpoint, there doesn’t appear to be a lot added worth in co-loading brokers that don’t goal the identical cell. Situations will be envisaged during which there will be profit, for instance, when co-delivering a vascular disrupting agent along with a chemotherapy drug in a nanoparticle that allows temporally managed launch kinetics, with the previous agent being launched first, to trigger tumour vascular shutdown, and the latter agent being launched afterwards, to limit cytotoxicity results to the tumour compartment and attenuate systemic aspect effects43.
Conceptually and scientifically, multi-drug nanomedicine therapies are elegant and interesting. The potential of with the ability to co-deliver a couple of lively pharmaceutical ingredient to the identical website or cell within the physique on the identical cut-off date opens up many therapeutic alternatives. These go method past most cancers, encompassing for instance, additionally the co-delivery of three–4 antiviral medicine for HIV or tuberculosis remedy, or the co-delivery of siRNAs, miRNAs, mRNAs and/or sgRNAs for optimized protein alternative remedy, gene silencing or gene editing11,44,45,46.
To create medical affect, will probably be essential to align scientific and conceptual nanotechnology engineering advances with rational pharmacological mechanisms and life like medical situations. The multi-drug nanomedicine subject continues to be in its infancy, with solely Vyxeos available on the market, and just a few double-drug formulations in medical growth. It’s anticipated that within the years to return, multi-drug nanomedicines will achieve extra traction. From a pharmaceutical know-how and industrial growth standpoint, they’re very interesting, as there nonetheless is a variety of mental property and medical software area to say. Based mostly on the result of our meta-analysis, and on the above-discussed insights and alternatives, we conclude that multi-drug nanomedicine holds important promise for purposes in oncology and past.




